While loop
The syntax of the while loop is:while (testExpression)
{
// statements inside the body of the loop
}How while loop works?
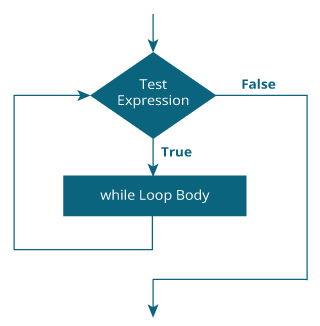
- The while loop evaluates the test expression inside the parenthesis ().
- If the test expression is true, statements inside the body of while loop are executed. Then, the test expression is evaluated again.
- The process goes on until the test expression is evaluated to false.
- If the test expression is false, the loop terminates (ends).
To learn more about test expression (when the test expression is evaluated to true and false), check out relational and logical operators.
Flowchart of while loop
Example 1: while loop
// Print numbers from 1 to 5
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5)
{
printf("%d\n", i);
++i;
}
return 0;
}Output
1
2
3
4
5
Here, we have initialized i to 1.
- When i is 1, the test expression i <= 5 is true. Hence, the body of the while loop is executed. This prints 1 on the screen and the value of i is increased to 2.
- Now, i is 2, the test expression i <= 5 is again true. The body of the while loop is executed again. This prints 2 on the screen and the value of i is increased to 3.
- This process goes on until i becomes 6. When i is 6, the test expression i <= 5 will be false and the loop terminates.
do...while loop
The do..while loop is similar to the while loop with one important difference. The body of do...while loop is executed at least once. Only then, the test expression is evaluated.
The syntax of the do...while loop is:
do
{
// statements inside the body of the loop
}
while (testExpression);How do...while loop works?
- The body of do...while loop is executed once. Only then, the test expression is evaluated.
- If the test expression is true, the body of the loop is executed again and the test expression is evaluated.
- This process goes on until the test expression becomes false.
- If the test expression is false, the loop ends.
Flowchart of do...while Loop
Example 2: do...while loop
// Program to add numbers until the user enters zero
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double number, sum = 0;
// the body of the loop is executed at least once
do
{
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%lf", &number);
sum += number;
}
while(number != 0.0);
printf("Sum = %.2lf",sum);
return 0;
}Output
Enter a number: 1.5
Enter a number: 2.4
Enter a number: -3.4
Enter a number: 4.2
Enter a number: 0
Sum = 4.70
Tags
C#